Dagger Cloud
Dagger Cloud requires a GitHub or Google account for identity verification. If you don't have one, register for a free GitHub account or create a free Google account before proceeding.
Dagger Cloud requires Dagger v0.11 or higher.
Organizations
A Dagger Cloud "organization" refers to a group of member accounts linked to a single team.
A member account grants a person access to log in to a Dagger Cloud organization to diagnose workflow failures and collaborate on changes. Deleting a member of a Dagger Cloud organization will not remove their runs and changes from Dagger Cloud.
You must hold the Admin role of a Dagger Cloud organization to administer members. You cannot change a member's role. Please contact Dagger Support via the in-app messenger for assistance if you need to change a member's role.
Create a Dagger Cloud organization
-
Sign up for Dagger Cloud by selecting a plan on the Dagger website. Dagger Cloud includes plans for both individuals and teams. Click
Continue with GitHubto log in with your GitHub account. -
After authorizing Dagger Cloud for your GitHub account, you'll create your organization.
Organization names may contain alphanumeric characters and dashes and are unique across Dagger Cloud. We recommend using your company name or team name for your organization.
-
Review and select a Dagger Cloud subscription plan.
-
If you selected the "Team" plan:
-
You will be presented with the option to add teammates to your Dagger Cloud account. This step is optional and not available in the Individual plan.
-
You will then enter your payment information. After your free 14 day trial completes, you will be automatically subscribed to the Dagger Cloud Team plan.
-
Traces
Connect to Dagger Cloud
The next step is to connect to Dagger Cloud from your local development environment or from your CI environment.
Connect from your local development host
You can visualize and debug your local Dagger workflow runs with Dagger Cloud to identify issues before pushing them to CI.
To configure for local development, run the dagger login command.
To use Dagger Cloud locally when you have multiple organizations linked to your account, you must use dagger login ORGANIZATION-NAME instead.
The Dagger CLI will invite you to authenticate your device by displaying a link containing a unique key. Click the link in your browser, and verify that you see the same key in the Dagger Cloud Web interface.
$ dagger login
Browser opened to: https://auth.dagger.cloud/activate?user_code=XXXX-YYYY
Confirmation code: XXXX-YYYY
Once you confirm your authentication code, your Dagger CLI will be authenticated and you can now visualize and debug your local Dagger workflow runs.
If you do not want to use dagger login, set your Dagger Cloud token as an environment variable. For example:
export DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN={your token}
Connect from your CI environment
To connect to Dagger Cloud from a CI environment, you require a Dagger Cloud token. Dagger Cloud creates this token automatically when you sign up.
To find your token, navigate to the settings page using the cogwheel icon in the top navigation bar. Under the Tokens sub-menu, click the eye icon to view the token. You can also use this URL pattern: https://v3.dagger.cloud/{Your Org Name}/settings?tab=Tokens
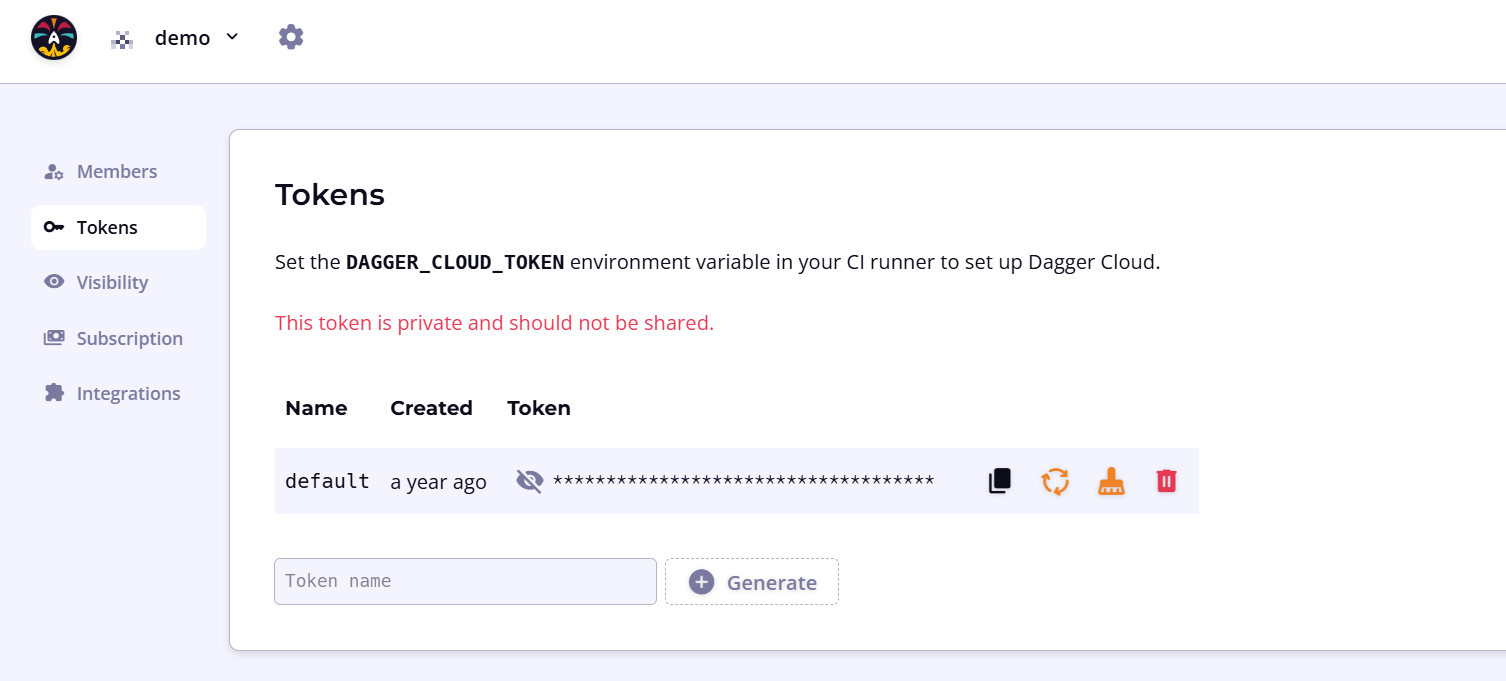
If you regenerate your token, you must replace the token wherever you've referenced it. To reduce operational interruptions, only regenerate your token if it has leaked.
Once you have your token, you can use it to connect Dagger Cloud with your CI environment. The general procedure is:
- Add your Dagger Cloud token to your CI environment.
- Store the Dagger Cloud token as a secret with your CI environment.
You must store the Dagger Cloud token as a secret (not plaintext) with your CI environment and reference it in your CI workflow. Using a secret is recommended to protect your Dagger Cloud account from being used by forks of your project. We provide links in the steps below for configuring secrets with popular CI tools.
- Add the secret to your CI environment as a variable named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN. - If you are using GitHub Actions, install the Dagger Cloud GitHub app for GitHub Checks. This app adds a GitHub check to your pull requests. Each check links to the corresponding workflow visualization in Dagger Cloud.
You can use Dagger Cloud whether you're hosting your own CI runners and infrastructure or using hosted/SaaS runners.
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI
- CircleCI
- Jenkins
- Argo Workflows
-
Create a new secret for your GitHub repository named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN, and set it to the value of the token. Refer to the GitHub documentation on creating repository secrets. -
Update your GitHub Actions workflow and add the secret to the Dagger workflow step as an environment variable. The environment variable must be named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKENand can be referenced in the workflow using the formatDAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN }}. Refer to the GitHub documentation on using secrets in a workflow.[See an example of a sample GitHub Actions workflow file]
-
Install the Dagger Cloud GitHub App. Once installed, GitHub automatically adds a new check for your GitHub pull requests, with a link to see CI status for each workflow job in Dagger Cloud.
-
Create a new CI/CD project variable in your GitLab project named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN, and set it to the value of the token. Ensure that you configure the project variable to be masked and protected. Refer to the GitLab documentation on creating CI/CD project variables and CI/CD variable security. -
Update your GitLab CI workflow and add the variable to your CI environment. The environment variable must be named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN. Refer to the GitLab documentation on using CI/CD variables.[See an example of a sample GitLab workflow file]
-
Create a new environment variable in your CircleCI project named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKENand set it to the value of the token. Refer to the CircleCI documentation on creating environment variables for a project. -
For GitHub, GitLab or Atlassian Bitbucket source code repositories only: Update your CircleCI workflow and add the following values to the CI environment. Refer to the CircleCI documentation on using pipeline values.
GitHub:
environment:
CIRCLE_PIPELINE_NUMBER: << pipeline.number >>GitLab:
environment:
CIRCLE_PIPELINE_NUMBER: << pipeline.number >>
CIRCLE_PIPELINE_TRIGGER_LOGIN: << pipeline.trigger_parameters.gitlab.user_username >>
CIRCLE_PIPELINE_REPO_URL: << pipeline.trigger_parameters.gitlab.repo_url >>
CIRCLE_PIPELINE_REPO_FULL_NAME: << pipeline.trigger_parameters.gitlab.repo_name >>Atlassian BitBucket:
environment:
CIRCLE_PIPELINE_NUMBER: << pipeline.number >>[See an example of a sample CircleCI workflow]
-
Configure a Jenkins credential named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKENand set it to the value of the token. Refer to the Jenkins documentation on creating credentials and credential security. -
Update your Jenkins Pipeline and add the variable to the CI environment. The environment variable must be named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKENand can be referenced in the Pipeline environment using the formatDAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN = credentials('DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN'). Refer to the Jenkins documentation on handling credentials.
- This Jenkins Pipeline assumes that the Dagger CLI is pre-installed on the Jenkins runner(s), together with other required dependencies.
- If you use the same Jenkins server for more than one Dagger Cloud organization, create distinct credentials for each organization and link them to their respective Dagger Cloud tokens.
- Typically, Jenkins servers are non-ephemeral and therefore it is not necessary to adjust the
docker stoptimeout. :::
-
Create a new Kubernetes secret named
dagger-cloudand set it to the value of the token. An example command to achieve this is shown below (replace theTOKENplaceholder with your actual token value). Refer to the Kubernetes documentation on creating secrets.kubectl create secret generic dagger-cloud --from-literal=token=TOKEN -
Update your Argo Workflows specification and add the secret as an environment variable. The environment variable must be named
DAGGER_CLOUD_TOKEN.[See an example of a sample Argo Workflows specification]-workflows.mdx)
Test the integration
The next step is to test the integration with Dagger Cloud.
Test from your local development host
- In your terminal, call a Dagger Function. You will see a Dagger Cloud URL printed in the terminal.
- Click on the URL to view details of the run in Dagger Cloud.
dagger -m github.com/shykes/daggerverse/hello@v0.3.0 call hello
Test from your CI environment
Trigger your CI workflow by pushing a commit or opening a pull request.
Public traces
Dagger Cloud automatically detects if the traces produced by your workflows originate from a CI system and a public repository. When both conditions are met, Dagger Cloud allows public access to these traces without requiring an invitation to the organization.
To modify this default setting, navigate to the organization page using the cogwheel icon in the top navigation bar. Under the Visibility sub-menu, click the eye icon to toggle public access to trace data as needed.
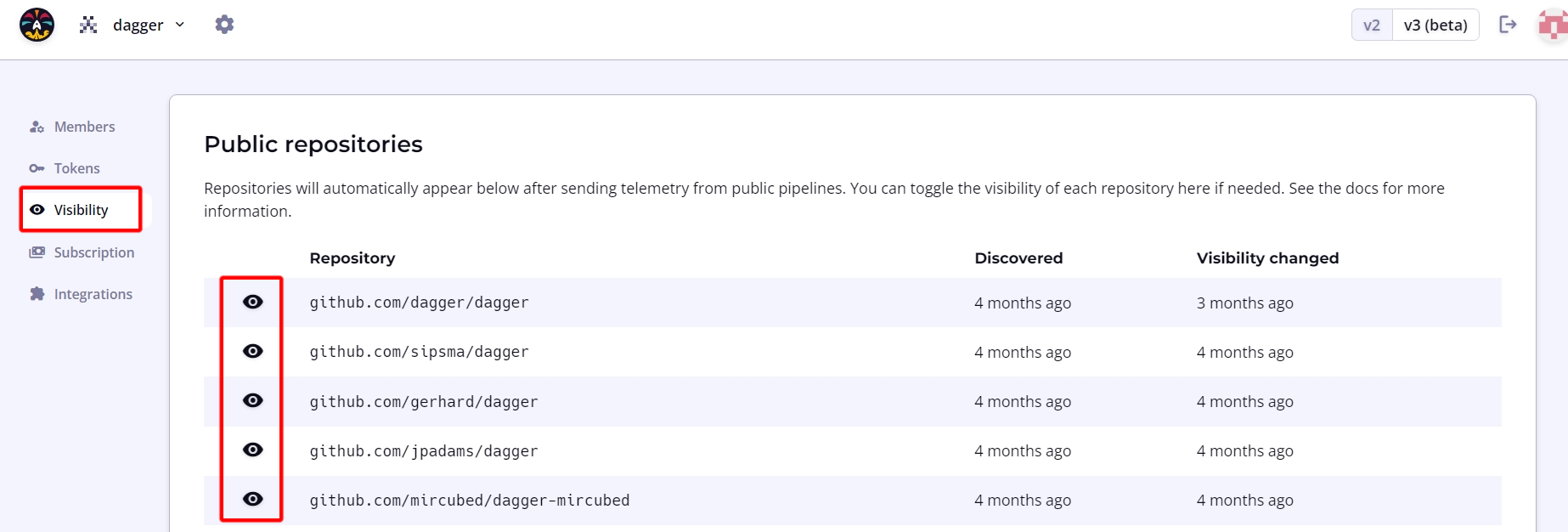
Make an individual trace public
Admin users can make an individual private trace public for sharing of links with users outside of your organization or who are not yet using Dagger Cloud. A confirmation step will verify your intention and the action is reversible.

Delete a trace
Admin users can delete an individual trace. There is a confirmation step before deletion, but after deletion, the trace will not be recoverable.

Modules
Dagger Cloud lets you see all your organization's modules in one place, with metadata like engine versions, descriptions, and linked repositories. Module information and activity is automatically synced from GitHub.
Add modules
Dagger Cloud scans your specified repositories for Dagger modules, showing them automatically in Dagger Cloud.
You must be signed in to Dagger Cloud with GitHub.
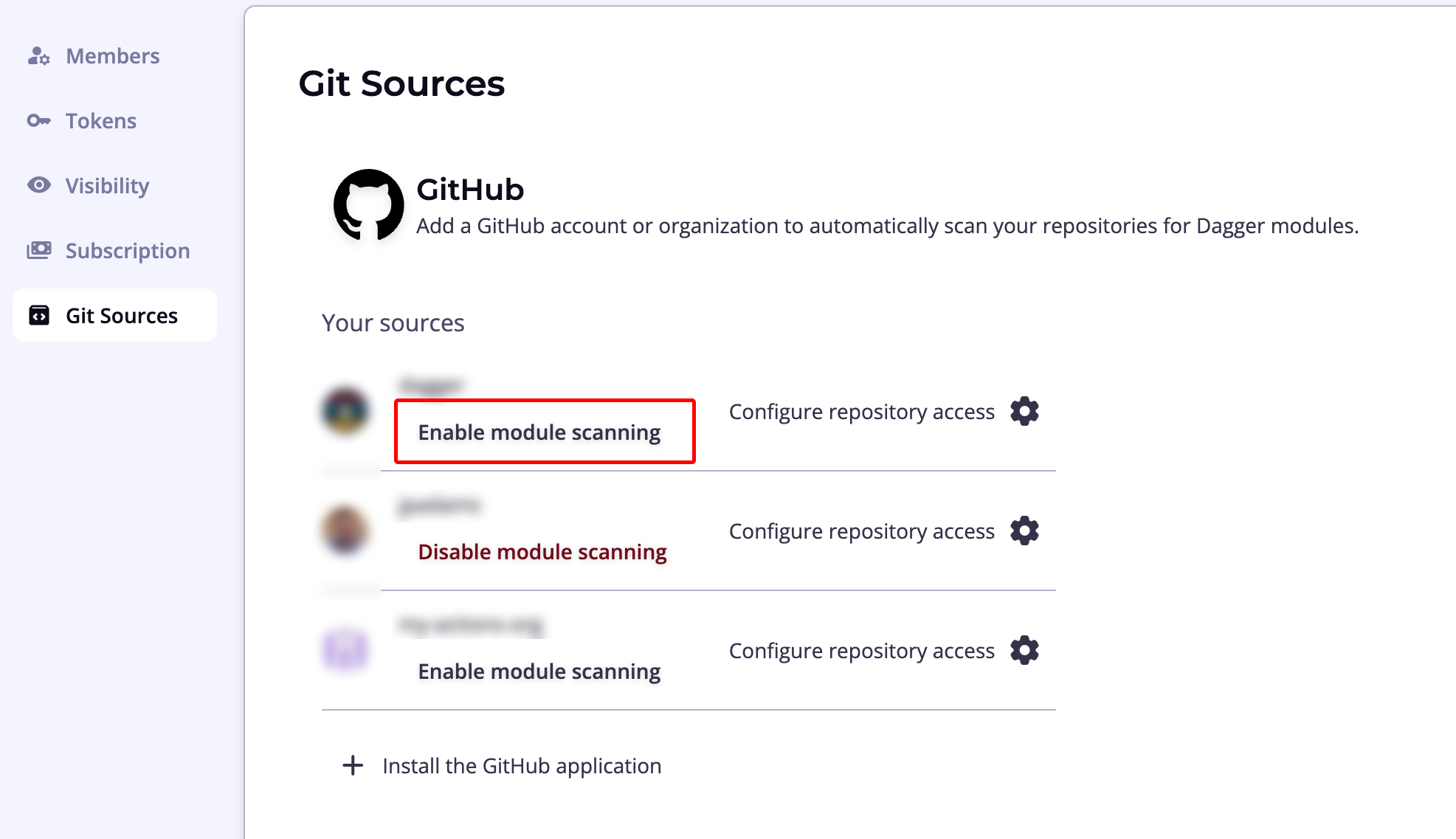
To initiate this process, navigate to the organization page using the cogwheel icon in the top navigation bar and select the Git Sources sub-menu. Click Install the GitHub Application to add a GitHub account or organization.
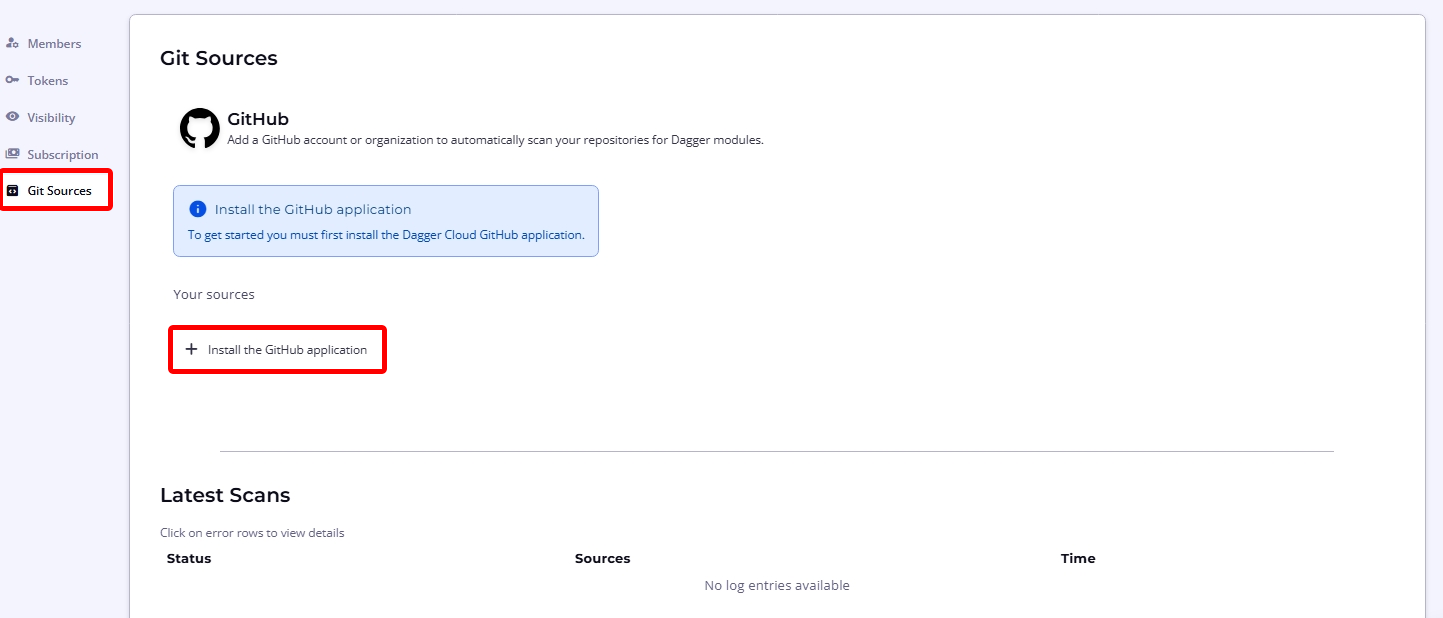
You will be directed to install the Dagger Cloud GitHub application and select the GitHub accounts and repositories to add.
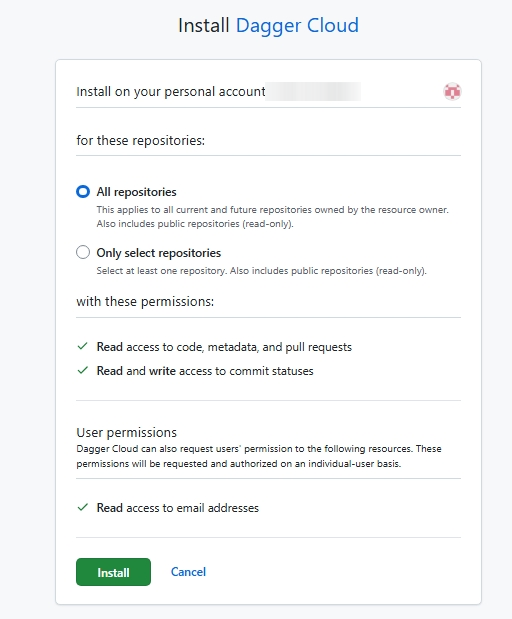
Complete the process and then, once the GitHub account or organization appears in the Dagger Cloud user interface, click Enable module scanning to have Dagger Cloud begin scanning for Dagger modules. You can enable module scanning for multiple GitHub organizations. Each one can be enabled on a single Dagger organization.
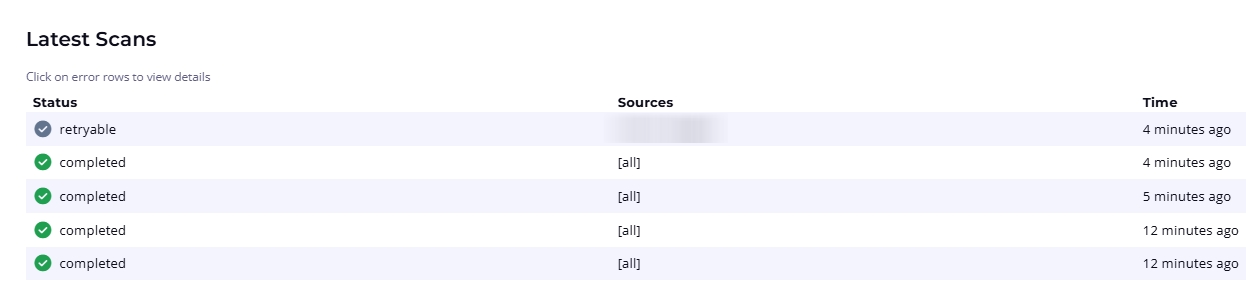
The Scan Results section at the bottom of the page maintains a record of scans and their status.
Manage and inspect modules
Once your modules have been added, you can start using Dagger Cloud to manage them.
Access the modules dashboard from the Modules menu item in the top navigation bar to see a list of available modules.
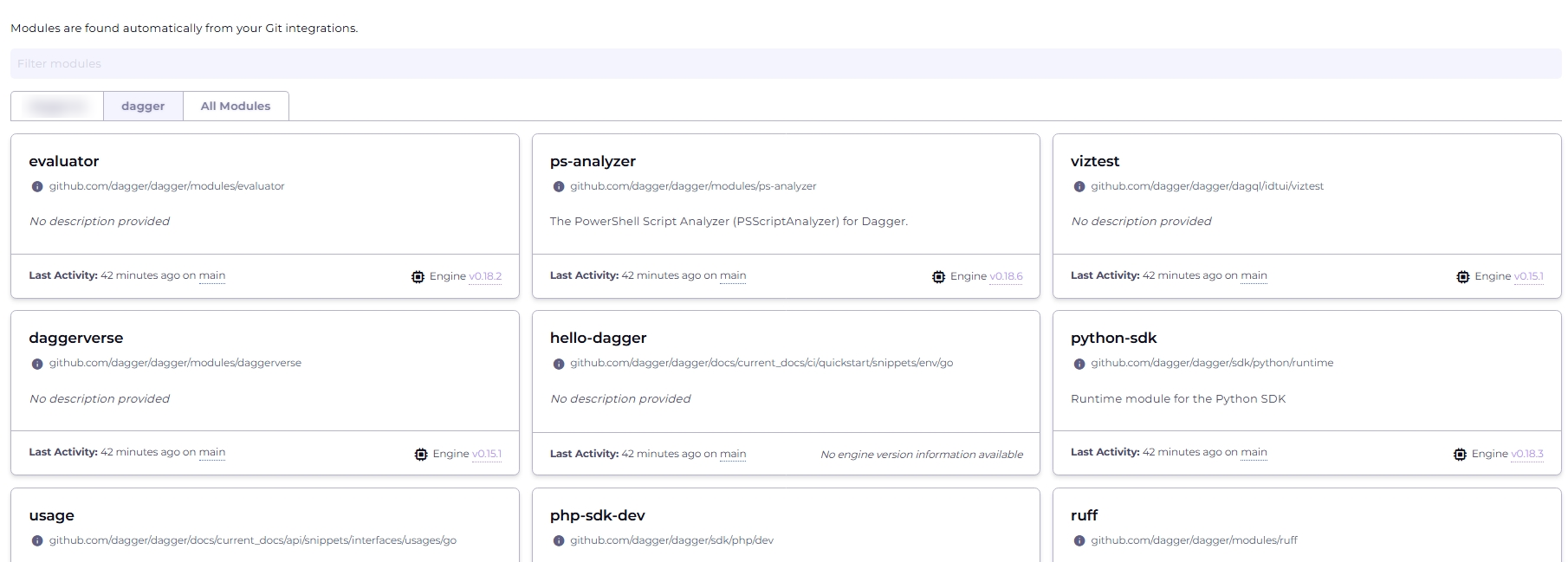
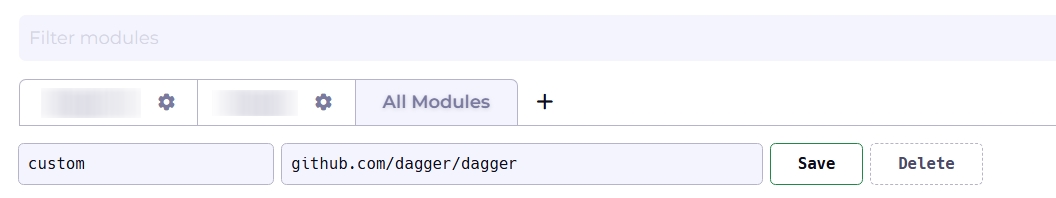
You can view your entire list of modules by selecting the All Modules tab. If you wish to curate and organize this list, you can create custom views of modules filtered by team, service, or domain. To create a custom view, click the + icon.
Select a module to see detailed information on its activity and API.
- API: View detailed API documentation for each module, including its installation command, functions, arguments and return values
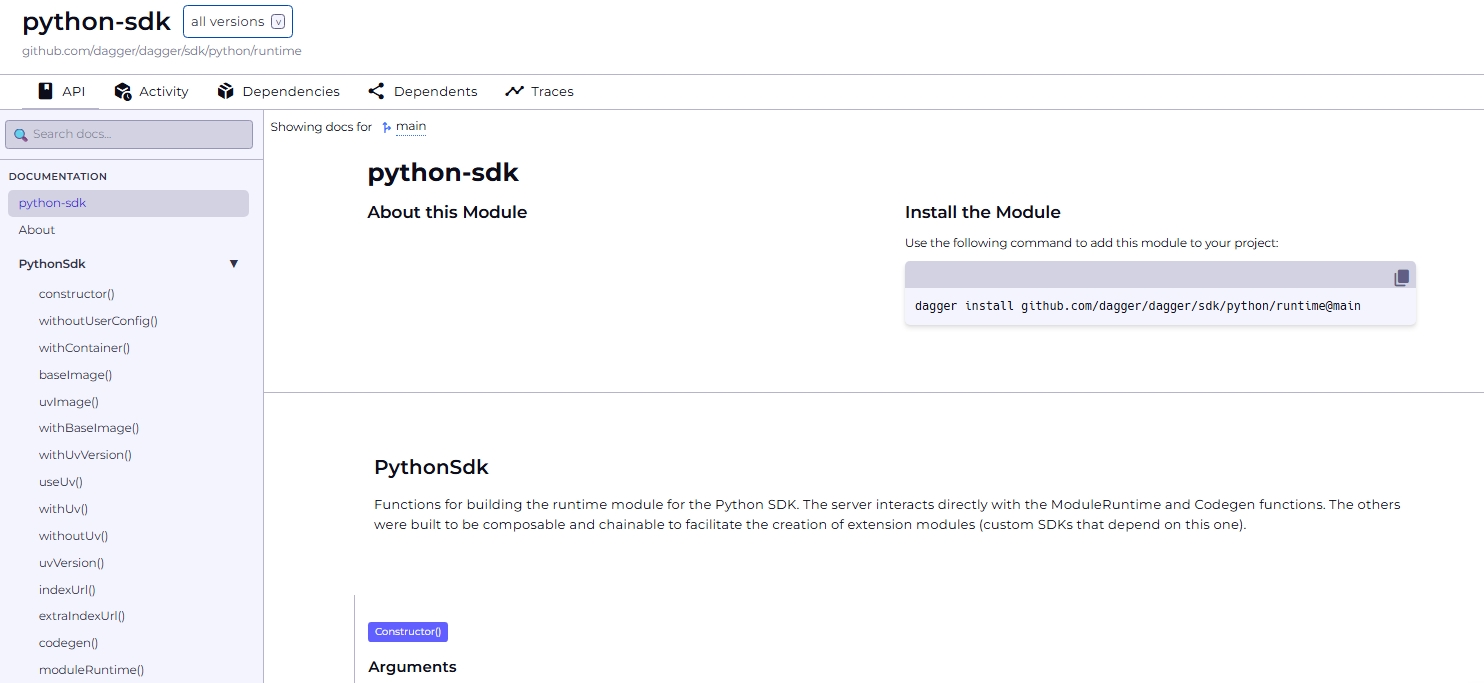
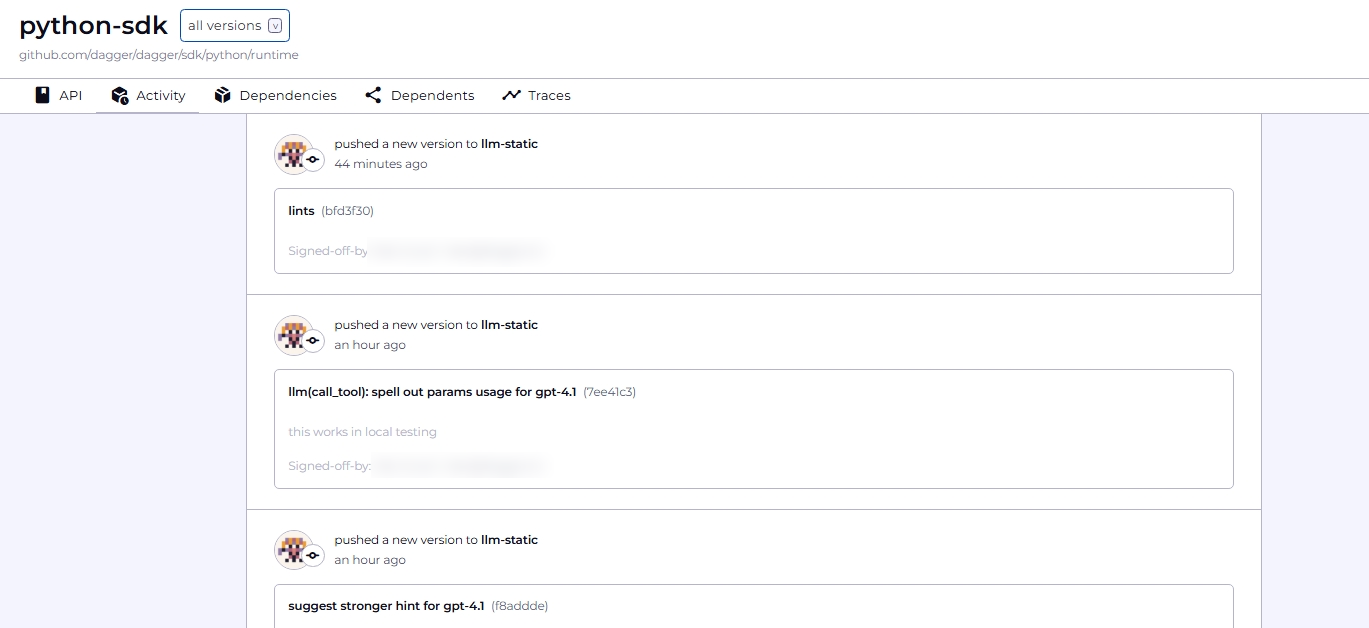
- Activity: See a list of commits, sorted by date
- Dependencies and dependents: Trace dependencies and dependents of your module

- Traces: List traces triggered by a module
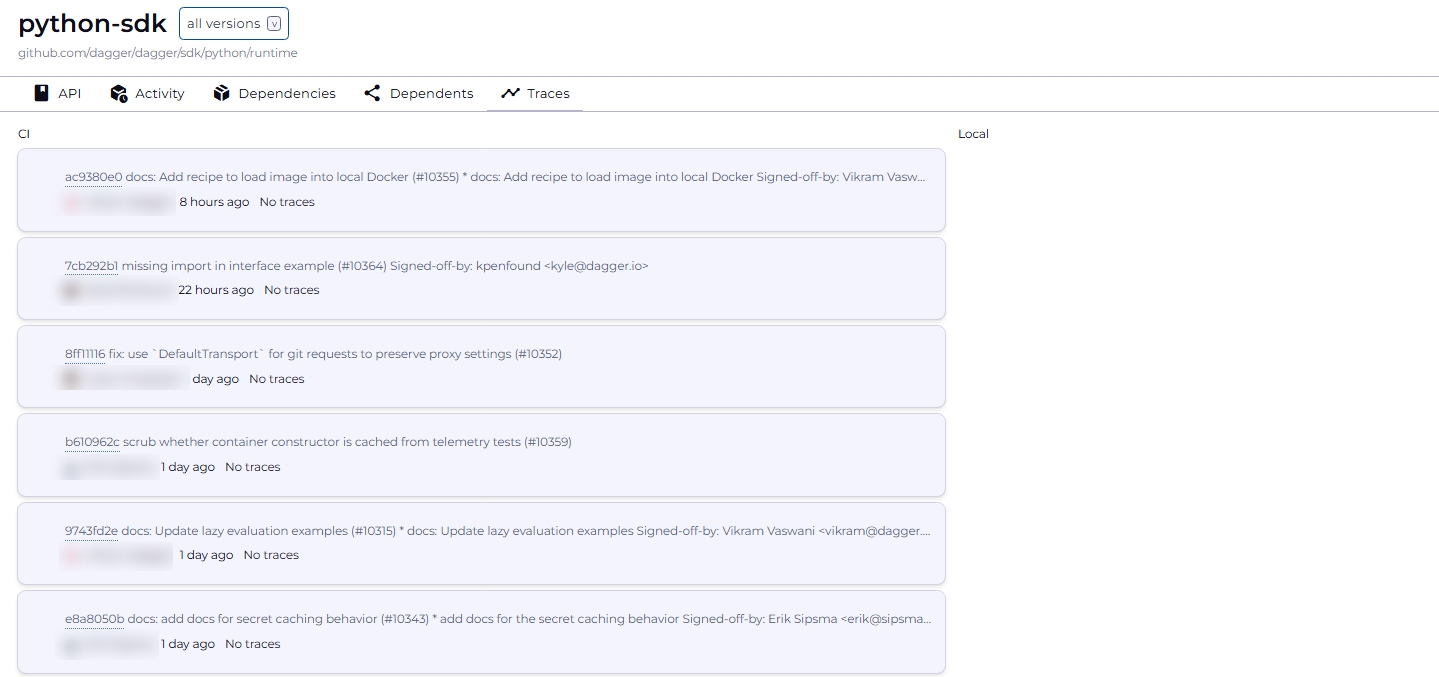
This information is available for all versions of the module; use the version selector in the top bar to switch between versions.
Roles and permissions
In Dagger Cloud, users can have one of two roles: Admin or Member. The Admin role is not a superset of the Member role. If a user needs to administer an organization and view Dagger workflow runs, ensure that the user also has the Member role.
| Actions | Admin | Member |
|---|---|---|
| View Dagger workflow runs and changes | ✓ | |
| View members of an org | ✓ | ✓ |
| Invite new members to an org | ✓ | |
| Delete an existing member from an org | ✓ | |
| Make an individual trace public | ✓ | |
| Delete an individual trace | ✓ |
You cannot change a member's role at this time. Please contact Dagger via the support messenger in Dagger Cloud if you need assistance.
Cache pruning
Within a Dagger Cloud organization, it is possible to prune the Dagger Cloud cache for a specific token. Navigate to the organization page using the cogwheel icon in the top navigation bar, select the Tokens sub-menu, and click the broom icon for the corresponding token.
